Age Range: 7-8 years old
Time: 45 minutes
Lesson Number: 2
Learning Objectives:
- Understand the basic concept of multiplication.
- Memorize the multiplication table from 2 to 12.
- Develop the ability to quickly calculate multiplication results.
- Enhance problem-solving skills using various methods for multiplication.
- Recognize real-life situations where multiplication is applied.
- Gain experience collaborating with peers to solve multiplication problems.
Universal Design For Learning (UDL):
Multiple Means of Engagement:
- Provide choices to increase motivation.
- Foster a supportive learning environment.
- Encourage self-regulation and goal-setting.
Essential Questions:
- What are the patterns and relationships in the multiplication table?
- How can understanding multiplication help us solve real-world problems?
- In what ways can we use different strategies to memorize multiplication facts effectively?
Materials and Technology:
- Internet
- Paper
- Pencil
Prior Knowledge:
- Basic Addition Skills: Students should be familiar with addition, as it forms the foundation for understanding multiplication.
- Understanding of Groups: Recognition of multiplication as repeated addition
- Familiarity with Numbers: Comfort with numbers 1 through 12 and their basic properties.
Pre-class Preparation:
- Create multiplication flashcards for numbers 2 to 12.
- Arrange seating for group activities and discussions to foster collaboration.
Lesson Plan Sequence:
Introduction:
This lesson sets a positive tone for the lesson, engages students, and prepares them for learning the multiplication table.
Instructional Content:
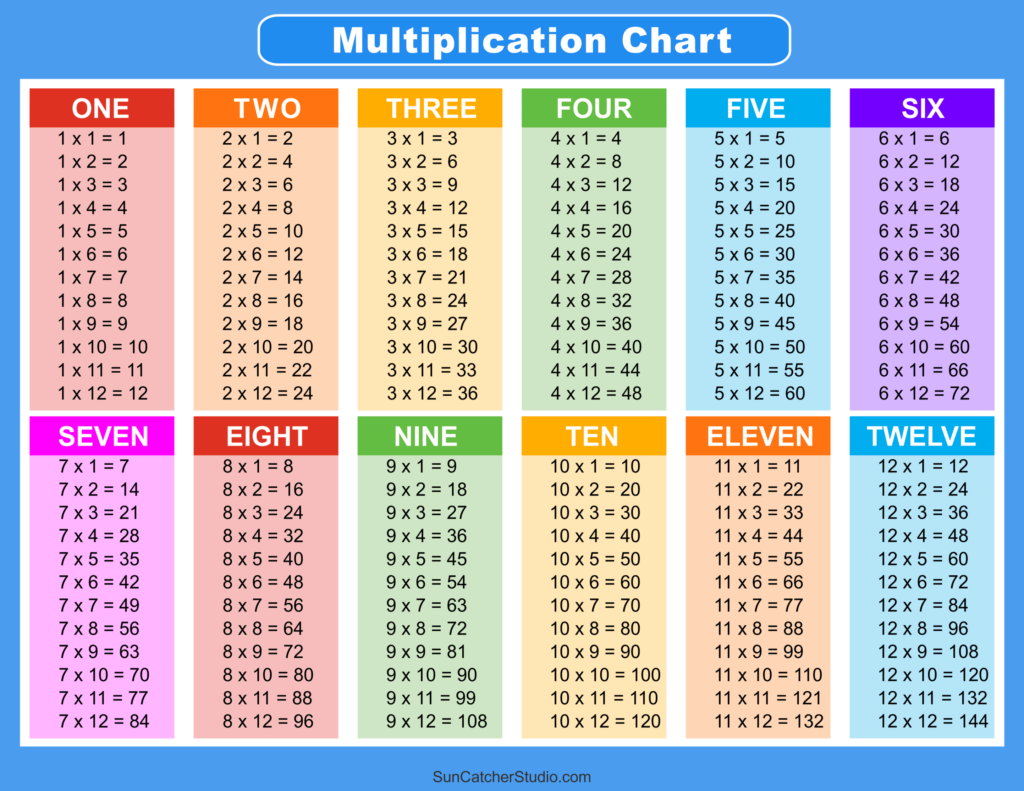
The ways to memorize multiplication table:
- Practice skip counting by the numbers in the multiplication table
- Identify patterns in the multiplication table
- Use flashcards with multiplication problems on one side and answers on the other
- Pair up with a classmate and teach each other the multiplication facts
Application:
Present students with real-life scenarios that require multiplication to solve, such as asking them how many pencils they would have if they bought three packs containing twelve pencils each, or how many apples they would have if they had four bags with six apples in each.
Interactive Learning Activity:
Setup: Divide the class into small teams and place flashcards at one end of the classroom.
Gameplay: Teams line up at the opposite end. When the timer starts, the first student races to pick a flashcard, solves the problem, and shouts the answer to their team. If correct, they score a point; if incorrect, they return to try again.
Wrap-Up: Continue until all cards are answered or time runs out, then tally points and discuss any challenging problems.
Conclusion:
In today’s lesson on memorizing the multiplication table from 2 to 12 has equipped students with essential strategies to understand and recall multiplication facts.
Assessment Overview:
| Letter Grade | Percentage | Achievement Requirement |
| A+ | 90 – 100% | The student engages well with the topic and demonstrates an excellent understanding of the course material through the completion and correctness of learning activities. Students go above and beyond the course material presented. |
| A | 85 – 89% | The student engages with the topic well. They completed the learning activity and demonstrated great understanding of the course content through the completion and correctness of learning activities. |
| A- | 80 – 84% | The student engages with the topic well and completes all learning activities. Some aspects of the course content understanding is missing from learning activities. |
| B+ | 77 – 79% | The student has completed all required work. The student demonstrates an okay understanding of the course content through the completion and correctness of learning activities. |
| B | 73 – 76% | The student has completed all required work and demonstrated some understanding of the course content. |
| B- | 70 – 72% | The student has completed most of the required work and demonstrated understanding of the content. |
| C+ | 65 – 69% | The student has completed most of the learning activity but does not demonstrate a thorough understanding of the material. |
| C | 60 – 64% | The student has not completed the learning activity but showed some engagement with the course material. |
| D | 50 – 59% | The student has not completed the learning activity or engaged with the lesson material. |
| F | 0 – 49% | Student has not engaged with the course content at all. |
References
- Van de Walle, J. A., Karp, K. S., & Bay-Williams, J. M. (2013). Elementary and middle school mathematics: Teaching developmentally. Pearson.
- Education.com. (n.d.). Multiplication worksheets and games. https://www.education.com

